The City of Summerside’s electric utility, Summerside Electric, is anticipating growth in customers’ peak capacity needs. Before investing in a planned diesel generator, the City asked Dunsky to conduct a capacity planning study, and to recommend the most effective approach to address peak capacity needs over the next 15 years.
Dunsky reviewed Summerside Electric’s technical, financial, and regulatory needs; assessed supply and demand-side resource options (including emerging technologies) going forward; and considered the utility’s strategic and other requirements. We also led consultations with numerous local stakeholders, through both targeted group and public sessions, to ensure our study reflected the needs and concerns of local residents and businesses.
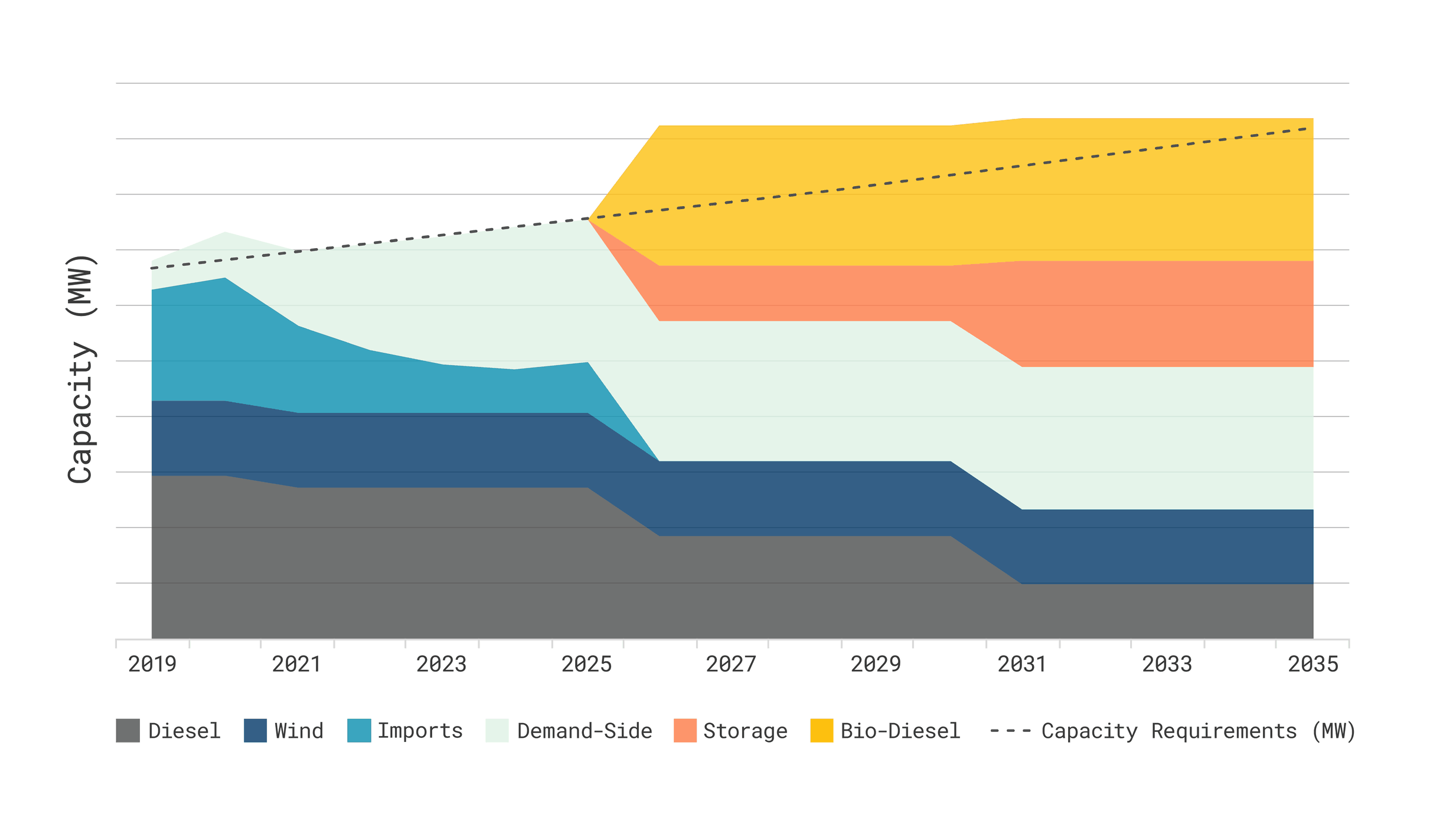
After assessing options, we recommended the City implement a “stacked, staged” approach to addressing its capacity needs. Rather than investing in a single, capital-intensive plant to meet short-term needs, we found an evolving strategy that stacks multiple, smaller options – including DR, utility scale storage and biodiesel – will provide greater flexibility at reduced cost and risk.
Specifically, we recommended:
- 2020: Expand demand-side capacity programs, including the city’s Heat-for-Less-Now (customer rate rebates in return for installing an electric thermal storage, or ETS system) and its large-customer interruptible load program;
- 2023-2025: Launch a utility-scale battery storage pilot;
- 2025: Plan for a biodiesel generator, but only if continued growth cannot be met by the DR and battery storage measures;
- 2028 & 2034: Refurbish existing wind farms as they reach end of life; and
- 2030: Expand battery storage based on results of the pilot and evolving battery pricing.
This plan enables a secure, reliable, and diverse resource mix while providing sufficient flexibility for Summerside Electric to adapt to fast-paced technological and policy changes. It will also allow Summerside to leverage significant anticipated cost reductions in battery storage in particular, while simultaneously pursuing electrification of heating and transportation uses, in line with the city’s climate ambitions.